Unit 21
G1: Understand the principles of video technology
Demonstrate understanding of Television standards using appropriate technologies
PAL (Phase Alternating Line)- Phase Alternating Line (PAL) is a colour encoding system for analogue television used in broadcast television systems in most countries broadcasting at 625-line / 50 field (25 frame) per second (576i).
SECAM (Séquentiel Couleur Avec Mémoire)- SECAM, also written SÉCAM ,Séquentiel couleur avec mémoire, French for "Sequential Color with Memory"), is an analog color television system first used in France.
Standards conversion- Television standards conversion is the process of changing one type of TV system to another. The most common is from NTSC to PAL or the other way around. This is done so TV programs in one nation may be viewed in a nation with a different standard. The TV video is fed through a video standards converter that changes the video to a different video system.
Widescreen aspect ratios-The aspect ratio of an image describes the proportional relationship between its width and its height. It is commonly expressed as two numbers separated by a colon, as in 16:9. For an x:y aspect ratio, no matter how big or small the image is, if the width is divided into x units of equal length and the height is measured using this same length unit, the height will be measured to be y units.
Component video signals- Component video is a video signal that has been split into two or more componentchannels. In popular use, it refers to a type of component analog video (CAV) information that is transmitted or stored as three separate signals.
High definition video- 1080p is a set of HDTV high-definition video modes characterized by 1080 horizontal lines of vertical resolution and progressive scan, as opposed to interlaced, as is the case with the 1080i display standard.
HDMI (High Definition Multimedia Interface)- HDMI (High-Definition Multimedia Interface) is a proprietary audio/video interface for transferring uncompressed video data and compressed or uncompressed digital audio data from an HDMI-compliant source device, such as a display controller, to a compatible computer monitor, video projector, digital television, or digital audio device. HDMI is a digital replacement for analog video standards.
DVI (Digital Visual Interface)- Digital Visual Interface (DVI) is a video display interface developed by the Digital Display Working Group (DDWG). The digital interface is used to connect a video source, such as a display controller to a display device, such as a computer monitor.
Broadcast systems- Broadcasting is the distribution of audio and/or video content to a dispersed audience via any electronic mass communications medium, but typically one using the electromagnetic spectrum (radio waves), in a one-to-many model. Broadcasting began with AM radio broadcasting which came into popular use starting with the invention of the crystal detector in 1906. Before this, all forms of electronic communication, radio, telephone, and telegraph, were "one-to-one", with the message intended for a single recipient. The term "broadcasting", borrowed from the agricultural method of sowing seeds in a field by casting them broadly about, was coined by either KDKA manager Frank Conrad or RCA historian George Clark[3] around 1920 to distinguish this new activity of "one-to-many" communication; a single radio station transmitting to multiple listeners.
Terrestrial broadcasting- Terrestrial television or broadcast television is a type of television broadcasting in which the television signal is transmitted by radio waves to the TV receiver from a terrestrial (Earth based) transmitter, a television station, and received with an antenna.
Satellite broadcasting-Satellite broadcasting is the distribution of multimedia content or broadcast signals over or through a satellite network.
Digital broadcasting-Digital broadcasting is the practice of using digital data rather than analogue waveforms for broadcasting over radio frequency bands. It is becoming increasingly popular as digital television (especially satellite television) but is having a slower adoption rate for radio where it is mainly used in Satellite radio.
Multiplexes- A system or signal involving simultaneous transmission of several messages along a single channel of communication.
Cable- Cable television is a system of delivering television programming to paying subscribers via radio frequency (RF) signals transmitted through coaxial cables or light pulses through fiber-optic cables.
Internet TV- Internet TV (ITV) is generally-available content distributed over the Internet. Unlike IPTV (Internet Protocol television), which is distributed over proprietary networks, Internet TV is available wherever a broadband connection exists. The two terms are often confused.
On demand systems Digital recording- Or Video on demand (display) (VOD) are systems which allow users to select and watch/listen to video or audio content when they choose to, rather than having to watch at a specific broadcast time. IPTV technology is often used to bring video on demand to televisions and personal computers.
Domestic-
Professional and broadcast formats- Video cameras like the one on the right are being used in the production of many of TV series and even for theatrical motion pictures.
Although there's a rather blurry line between professional and consumer formats, professional camcorders typically have many, but not necessarily all, of the following features:
Three imaging "chips" (Except for two professional 35mm motion picture sized chip cameras, consumer formats typically have only one). An audio level meter and the ability to control audio levels (i.e., you are not stuck with an AGC audio circuit). Low-impedance, balanced (i.e., professional quality) mic inputs. A jack for headphones so you can monitor audio with high-quality earphones. Detachable lenses so you can use special purpose lenses and aren't stuck with whatever zoom lens the manufacturer originally put on the camera. A video output for an external video monitor (You and others can see the video on a large, high-quality monitor). High-quality 4:2:2 digital signal processing
In some cases a dockable camcorder design where the camera can be fitted with (attached to) different recording devices.
Tape and hard drive recording- A hard disk recorder (HDR) is a type of direct-to-disk recording system that uses a high-capacity hard disk to record digital audio or digital video. Hard disk recording systems represent an alternative to more traditional reel-to-reel tape or cassette multitrack systems, and provide editing capabilities unavailable to tape recorders. The systems, which can be standalone or computer-based, typically include provisions for digital mixing and processing of the audio signal.
A tape drive is a data storage device that reads and writes data on a magnetic tape. Magnetic tape data storage is typically used for offline, archival data storage. Tape media generally has a favorable unit cost and a long archival stability.
Connection line-up and operation-
Camera set up for a specific location-The single-camera setup, or single-camera mode of production, also known as Portable Single Camera, is a method of filmmaking and video production.
A single camera — either motion picture camera or professional video camera — is employed on the set, and each shot to make up a scene is taken independently. An alternative "single camera" method that actually uses two cameras is more widely used. The latter method is intended to save time by using two cameras to capture a medium shot of the scene while the other can capture a close-up during the same take.
The multiple-camera setup, multiple-camera mode of production, multi-camera or simply multicam is a method of filmmaking and video production. Several cameras—either film or professional video cameras—are employed on the set and simultaneously record or broadcast a scene. It is often contrasted with single-camera setup, which uses one camera.
Colour temperature- The color temperature of a flat panel LCD or Plasma television is often a specification that many consumers are unaware of, or do fully understand. The color temperature of a flat panel TV is actually a very important technical consideration because it can drastically affect the way in which an image is displayed on the TV screen. Both cinematographers and photographers alike give great consideration to the color temperature of their images when shooting as it can substantially alter the perceived mood and atmosphere of the shot. Similarly, adjusting the color temperature on a television can, for example, greatly heighten the atmosphere of a film.
Lenses (exposure, focus) Digital editing- Cinematography is the science or art of motion-picture photography by recording light or other electromagnetic radiation, either electronically by means of an image sensor, or chemically by means of a light-sensitive material such as film stock. Typically, a lens is used to repeatedly focus the light reflected or emitted from objects into real images on the light-sensitive surface inside a camera during a questioned exposure, creating multiple images. With an electronic image sensor, this produces an electrical charge at each pixel, which is electronically processed and stored in a video file for subsequent display or processing. The result with photographic emulsion is a series of invisible latent images on the film stock, which are later chemically "developed"into a visible image. The images on the film stock are played back at a rapid speed and projected onto a screen, creating the illusion of a movie.
Cinematography finds uses in many fields of science and business as well as for entertainment purposes and mass communication.
File types-What is Video Codec?
A codec is a device or software that is used to compress or decompress a digital media file, such as a video or song.
The “codec” can be dividing into 2 parts: encode and decode. The encoder performs the compression (encoding) function and the decoder performs the decompression (decoding) function. Some codecs include both of these components and some codecs only include one of them.
For example, when you rip a song from an audio CD to your computer, the Player uses the Windows Media Audio codec by default to compress the song into a compact WMA file. When you play that WMA file (or any WMA file that might be streamed from a website), the Player uses the Windows Media Audio codec to decompress the file so the music can be played through your speakers.
What is the Difference between Video Codec and File Formats?
A file format is like a type of container. Inside the container is data that has been compressed by using a particular codec. And for a container that can obtain a different encoding format video and audio. And sometimes they have the same name.
File size- file size - Computer Definition. The length of a computer file in bytes. Following are common file types and sizes. See space/time, file and byte. KB=kilobytes MB=megabytes GB=gigabytes TB=terabytes FILETYPE APPROX.
Compression- ike file compression, the goal of media compression is to reduce file size and save disk space.
System compatibility-
Hardware- In information technology, hardware is the physical aspect of computers, telecommunications, and other devices. The term arose as a way to distinguish the "box" and the electronic circuitry and components of a computer from the program you put in it to make it do things. The program came to be known as the software.
Data transfer- Data transfer is the process of using computing techniques and technologies to transmit or transfer electronic or analog data from one computer node to another. Data is transferred in the form of bits and bytes over a digital or analog medium, and the process enables digital or analog communications and its movement between devices.
Data transfer is also known as data transmission.
File management- File management describes the fundamental methods for naming, storing and handling files. By using appropriate file and folder naming strategies, along with good metadata practice and catalog software, you can make the most of your image collection.
Develop a table, or similar, of different broadcasting systems, their differences and similarities
|
Broadcasting Systems |
What are they? |
Differences |
Similarities |
|
Satellite Broadcasting |
This is when signals are sent from a satellite to a TV station. |
Uses a space station to transmit signals which are that transmitted to earth through the use of a satellite dish. |
A similarity to terrestrial broadcasting is that both of them use external signal receivers. |
|
Digital Broadcasting |
This is the practice of using digital data rather than using analogue waveforms for broadcasting over radio frequency bands. |
Only makes use of digital signals. |
Earth bound. Like multiplexes it makes use of digital signals. |
|
Terrestrial Broadcasting |
This is a type of television broadcasting in which the television signal is transmitted by radio waves to the TV receiver from a terrestrial (Earth based) transmitter, a television station, and is received with an antenna. |
Uses pylons and TV aerials to transmit signals across a range of large areas. However, unlike the cable broadcasting system, this system still transmits signals through the atmosphere. |
Earth bound. A similarity to satellite broadcasting is that both of them use external signal receivers. This broadcasting system is similar to cable broadcasting as the terrestrial broadcasting system makes use of cables in order to connect their materials to each other, e.g. the TV aerial to the TV |
|
Cable |
Cable broadcasting is the use of underground cables to transmit signals from one place to another. |
This system uses physical materials to transmit the signals across a range of large areas underground. |
Earth bound. This broadcasting system is similar to terrestrial broadcasting as the system makes use of cables in order to connect their materials to each other, e.g. the TV aerial to the TV. |
|
Multiplexes |
Multiplexing is the act of combining many signals into a single transmission circuit or channel. |
This system makes use of multiple signals through the use of one transmission circuit. It can make use of analogue or digital signals. |
Like digital broadcasting it can make use of digital signals. |
|
Internet TV |
Internet TV is the use of the internet on a television screen. It is the ability to stream things from the internet on the TV. In technical terms it is the digital distribution of television content via the public internet. |
Internet TV uses Wifi to broadcast shows or films. |
This system is similar to the on demand system because it uses the internet to transmit and view content. |
|
On Demand Systems |
On demand systems are systems which allow the user to choose when they watch/listen to a video or audio content, rather than having to watch it at the specific broadcasting time. |
It can be viewed on many different devices. |
This system is similar to the internet TV system because it uses the internet to transmit and view content.
|
Create presentation on digital recording/editing- inc. specific examples
G2: Be able to use video recording technology
Record using different settings within the camera to record relevant footage for product
Record using a variety of locations and set-ups inc. studio and multi-camera techniques
G3: Be able to use video post-production technology:Use post-production systems to edit Work Evidence post-production practices inc. downloading digital material, file formats
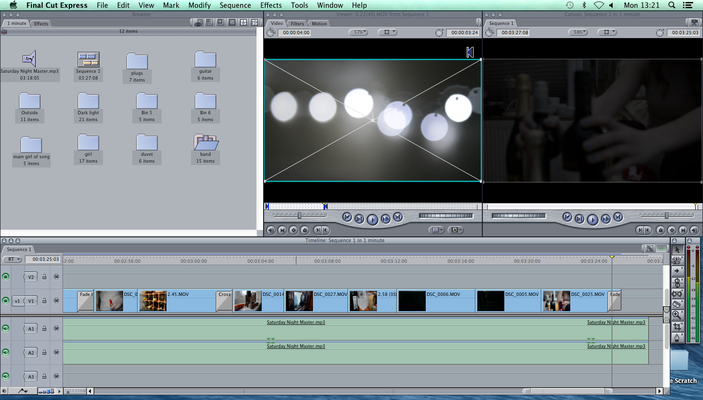
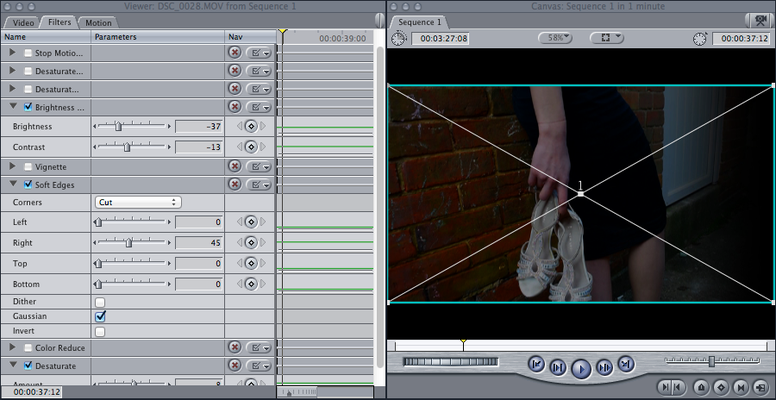
Use post-production systems to edit work
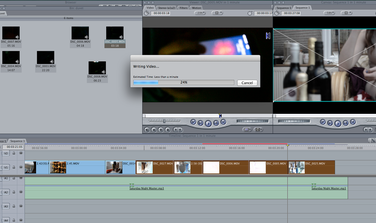
This shows me editing my footage that i had recorded previously
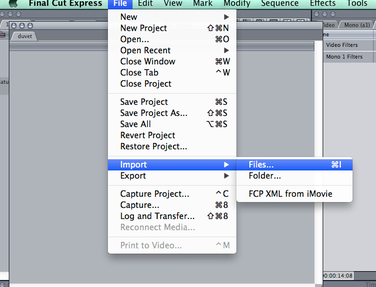
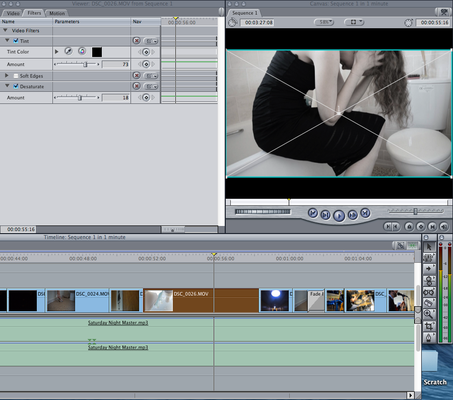
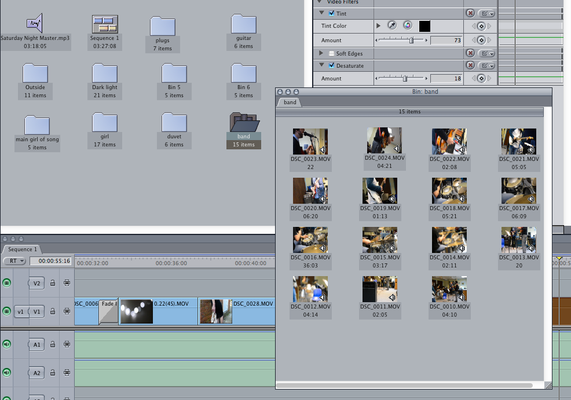
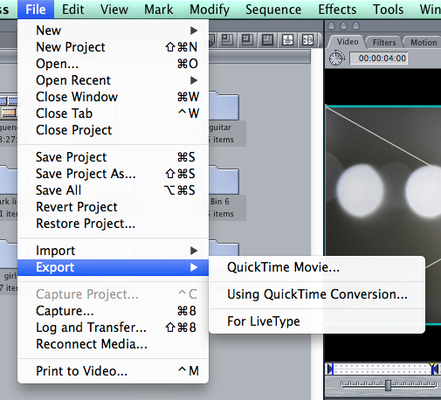
Evidence post-production practices inc. downloading digital material, file formats
This shows me editing and exporting the footage that i had recorded.